Laser cutting
Laser melting cutting: In laser melting cutting, the workpiece is partially melted and then the molten material is ejected with the help of nitrogen or air. Because the transfer of material only occurs in its liquid state, the process is called laser melt cutting, usually cutting stainless steel.
Laser flame cutting: Laser flame cutting differs from laser melting cutting in that oxygen is used as the cutting gas. With the help of the interaction between oxygen and heated metal, a chemical reaction occurs that further heats the material. Due to this, the cutting rates achievable with this method are higher than with melt cutting for the same thickness of structural steel. Usually cutting carbon steel.
Laser gasification cutting: During the laser gasification cutting process, the material vaporizes at the cutting seam. In this case, very high laser power is required.
- 1.Increased plate cutting limit thickness
- 2.Improved cutting efficiency, cutting 40mm carbon steel, the speed of 20KW is 133% higher than 12KW
- 3.Cost reduction, revenue increase
The advantages of high-efficiency laser cutting applications:
Comparison of Advantages between Traditional Cutting and Fiber Laser
Plasma Cutting
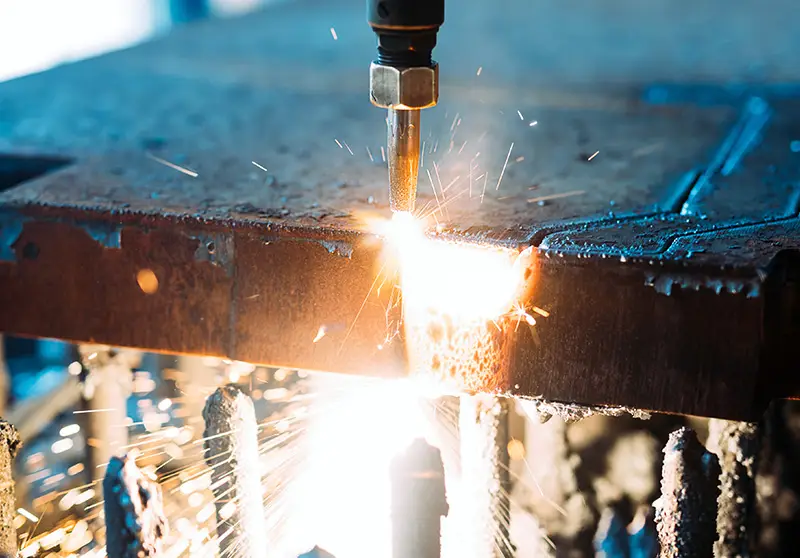 Plasma cutting can be used to cut metal, from thin to thick plates, with generally wider cutting seams and higher heat input into the parts, resulting in rough cutting surfaces
Plasma cutting can be used to cut metal, from thin to thick plates, with generally wider cutting seams and higher heat input into the parts, resulting in rough cutting surfacesLaser cutting
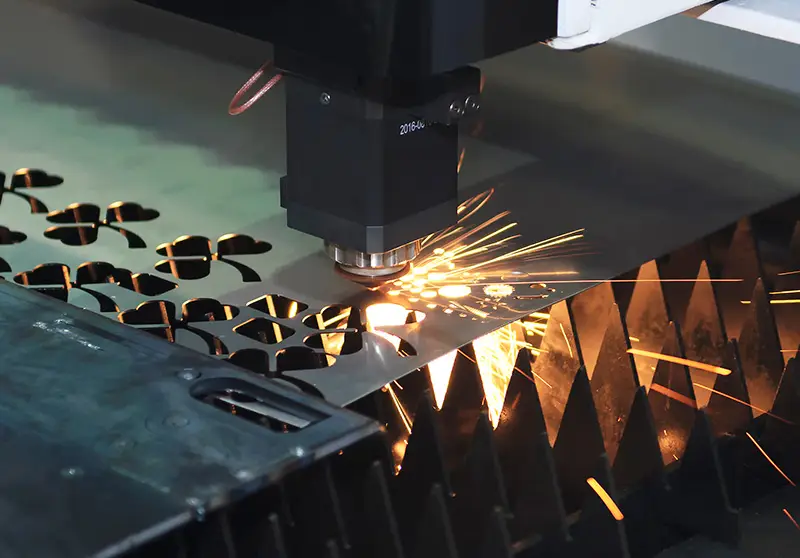 Laser cutting has higher cutting accuracy, quality, and speed, with almost no slag on the cutting section and consistent on all four sides
Laser cutting has higher cutting accuracy, quality, and speed, with almost no slag on the cutting section and consistent on all four sides
High pressure water cutting
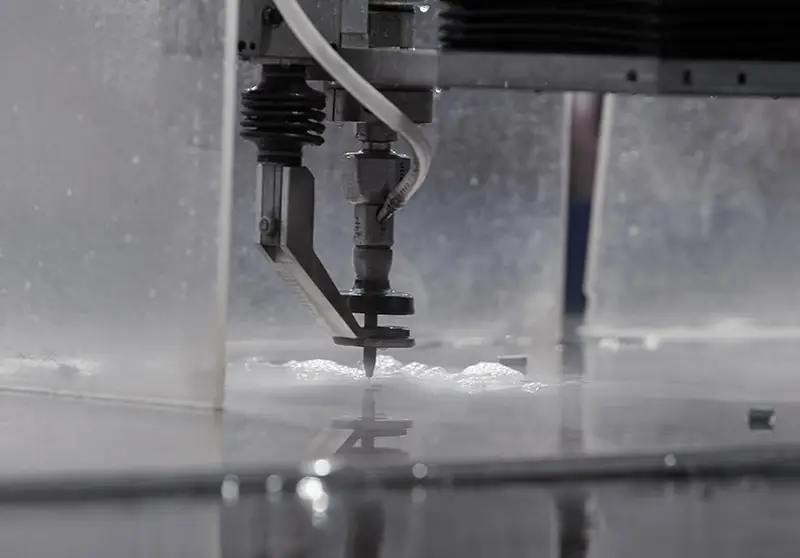 High pressure water cutting utilizes high-speed water jet cutting technology. When cutting high hardness or thick plates, the speed is very slow, energy consumption is high, and maintenance costs are high.
High pressure water cutting utilizes high-speed water jet cutting technology. When cutting high hardness or thick plates, the speed is very slow, energy consumption is high, and maintenance costs are high.Laser cutting
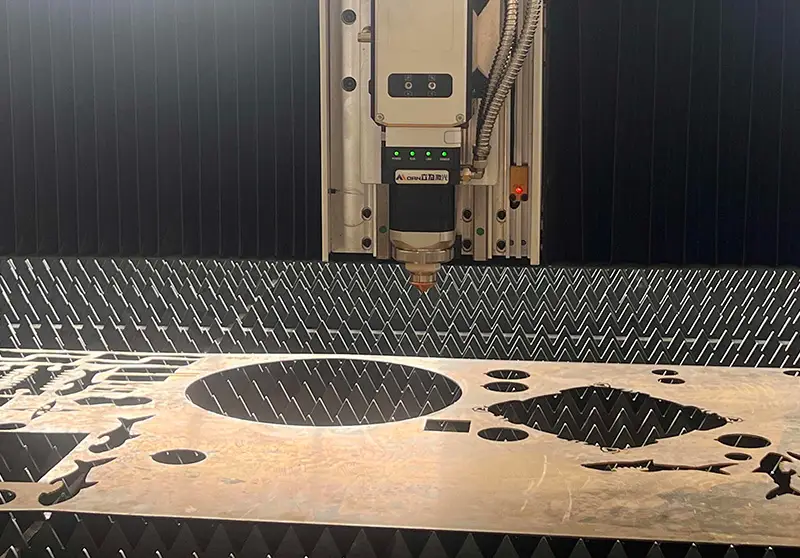 Laser cutting can cut metal sheets faster, with fast cutting speed. The 976 high-efficiency pump technology of Guanghui Laser has lower energy consumption and lower cost
Laser cutting can cut metal sheets faster, with fast cutting speed. The 976 high-efficiency pump technology of Guanghui Laser has lower energy consumption and lower cost
Wire cutting
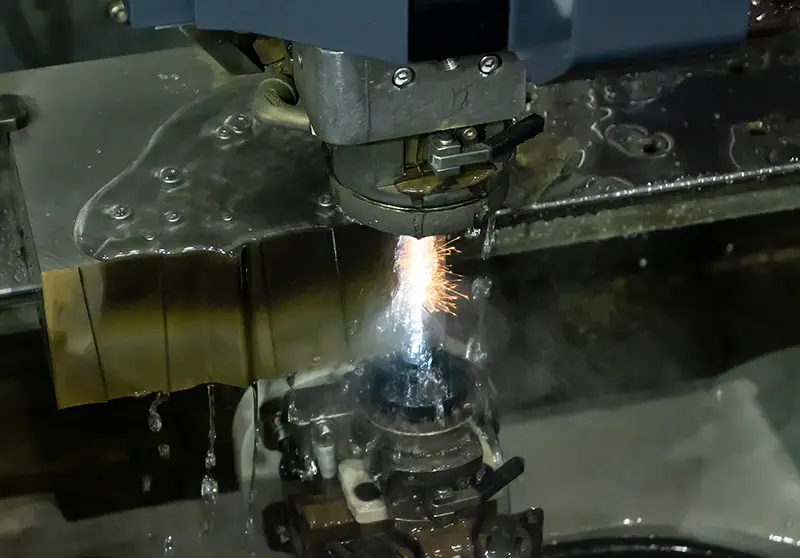 Wire cutting can only cut conductive materials, and requires cutting coolant during the cutting process, which is very slow. Sometimes, other methods such as perforation and threading are needed to cut, and the cutting size is greatly limited.
Wire cutting can only cut conductive materials, and requires cutting coolant during the cutting process, which is very slow. Sometimes, other methods such as perforation and threading are needed to cut, and the cutting size is greatly limited.Laser cutting
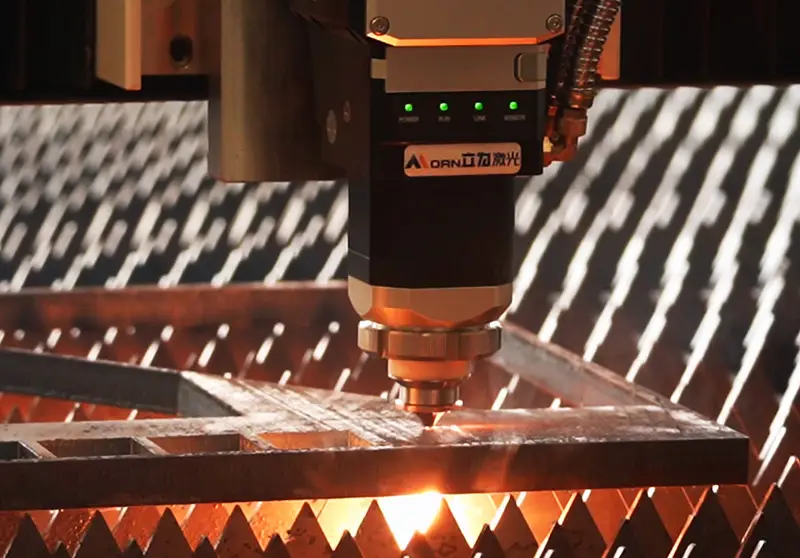 The application range of laser cutting machines is very wide, with small deformation of the sheet metal, fast cutting speed, and higher cutting efficiency,
The application range of laser cutting machines is very wide, with small deformation of the sheet metal, fast cutting speed, and higher cutting efficiency,
Application scenarios



